
The sites that are most commonly utilized for IM injections include the deltoid muscle of the shoulder the vastus lateralis of the thigh and the ventrogluteal, gluteus medius, or dorsogluteal muscles of the hip.
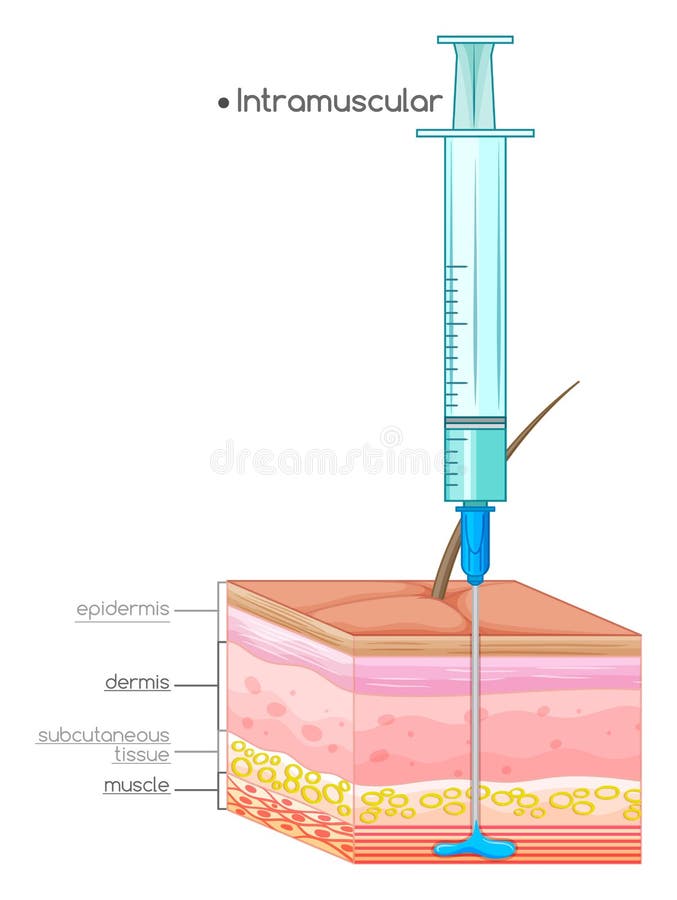
Also, if the patient has already received this injection, it is necessary to verify the injection site that was previously used and to ensure that the previous dose did not result in any adverse reactions. In addition, specifically for IM injections, it is important to assess the patient's muscle mass to determine the appropriate needle size. Some examples of medications that are commonly delivered by IM injections include antibiotics, hormones, and vaccinations.Īs in any other route of administration, the nurse must consider if the medication is appropriate, given the patient's medical conditions, allergies, and current clinical status. IM injections are recommended for patients unable to take oral medications and for uncooperative patients. Skeletal muscles have fewer pain-sensing nerves than subcutaneous tissue, which allows for the less painful administration of irritating drugs ( e.g., chlorpromazine, an anti-psychotic). Since muscle fibers are well perfused, this route of administration provides quick uptake of the medication and allows for the administration of relatively large volumes. Intramuscular (IM) injections deposit medications deep into the muscle tissue. Source: Madeline Lassche, MSNEd, RN and Katie Baraki, MSN, RN, College of Nursing, University of Utah, UT


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
